Topology optimization concept
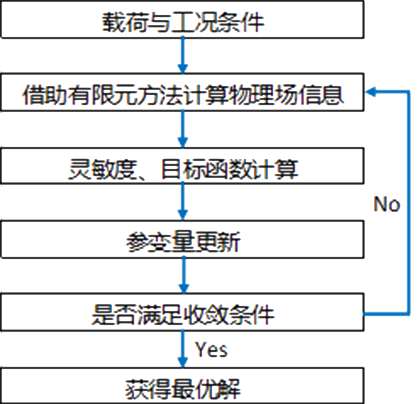
Topology optimization is the process of optimizing the layout and structure of materials based on a set of defined rules set by designers within a given 3D geometric design space. The goal is to maximize the performance of parts by mathematically modeling and optimizing factors such as external forces, load conditions, boundary conditions, constraints, and material properties within the design scope.
Topology optimization process - optimization steps
1. Determine the minimum design space required for the parts
2. Define input information such as external loads, boundary conditions, constraint conditions, and material properties.
3. Use FEA to consider the minimum set design network and decompose the design space into smaller regions.
four
Topology optimization uses finite element to create a basic mesh for this smaller design area, and evaluates the stress distribution and strain energy of the mesh through FEA to find the optimal load or stress that each element can handle.
5. Topology optimization programs apply stress to the design from various angles in a digital manner, evaluate its structural integrity, and identify areas of unwanted materials.
6. Test the stiffness, flexibility, stress, and deflection of each finite element according to the defined requirements, and determine the excess material area.
Finally, finite element analysis weaves the various components together to form the final design draft.
Advantages of Topology Optimization
Optimization design - Product design needs to balance various factors and determine the best design solution. FEA, because it can consider various factors in advance, can greatly avoid the possibility of design failure.
The minimization of material usage - the most attractive aspect of topology optimization is that it can reduce unnecessary weight. Especially in the aviation industry, adding one gram of weight requires a significant increase in design costs. Lighter weight and smaller size also mean less energy consumption.
Cost effective - Topology optimization can minimize material usage and costs to the greatest extent possible. And it also saves other factors such as packaging, less movement and transportation energy. The many complex geometric shapes generated by topology optimization can make standard manufacturing processes "difficult to implement", but as 3D printing technology becomes more mature, this design is not so difficult to implement.
Reducing Environmental Impact - Topology optimization can be defined as sustainable design as it minimizes the use of materials to the greatest extent possible.

Topology Optimization Case - Cabin hinge
In the aerospace field, 3D printing topology optimization technology can be used to produce lighter and stronger components, thereby reducing fuel consumption and improving flight efficiency. The titanium metal components used for 3D printing - cabin hinges - are also optimized for strength/weight ratio through topology optimization methods, and the design model is directly exported to the printer for production and processing through the AM manufacturing module. The combination of 3D printing and topology optimization can improve the strength, reduce weight, and lower costs of parts, which is one of the important technological trends in future industrial design and manufacturing, especially in the aerospace field.
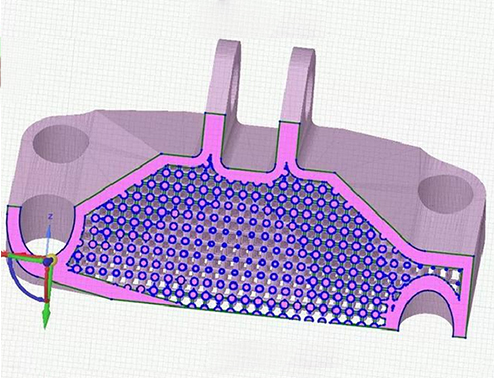
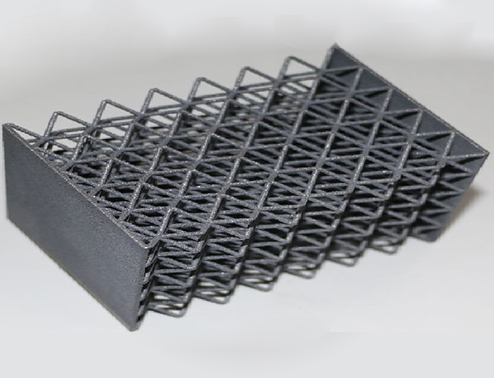
Lattice structure
Dot matrix structure can reduce the weight of products, and compared to physical structure, dot matrix structure can also reduce printing time. Optimize the structure of the product while meeting its stiffness requirements, reducing manufacturing and material usage costs. In addition, the lattice skin structure can serve as a support and shape control structure for easily deformed products such as thin-walled parts, improving the manufacturing quality of the products.
Lattice structure
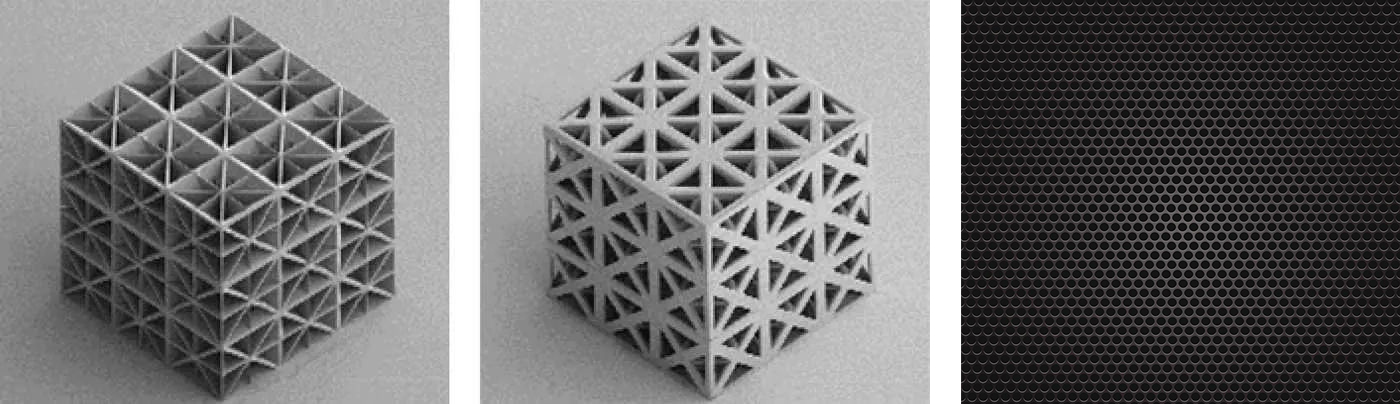
The porous lattice structure adopts parameterized design, which can quickly achieve lattices with different porosities and wall thicknesses through parameter driving, including face centered cubic lattice, body centered cubic lattice, octagonal framework structure, etc. The porous lattice structure can serve as an internal weight reduction structure for products, reducing the overall weight and cost of the product; It can also be used as an internal structure of energy storage devices, filling phase change materials between pores to achieve phase change energy storage, and through integrated additive manufacturing to achieve rapid prototyping of products, ensuring high quality and reliability of the products.
Lattice structure
Triple periodic minimal surface (TPMS) is a type of three-dimensional surface structure with periodic repeating elements. In the field of engineering, TPMS structures are widely used in materials science, biomedical engineering, energy storage, and other fields due to their unique properties. Its main characteristics are smooth surface, high connectivity, and excellent mechanical properties. The design of TPMS allows for direct control of the basic performance of the structure through parameters in mathematical expressions, enabling the design of different porosity, wall thickness, and gradient structures.

Thermal Simulation
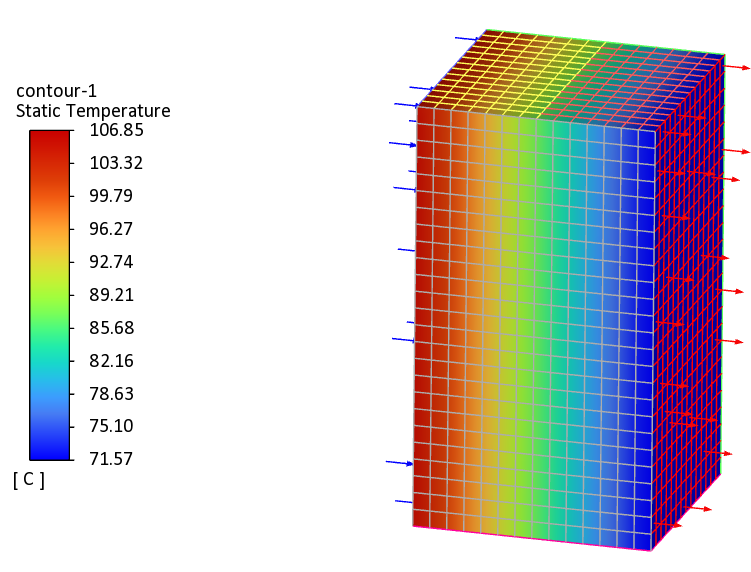
Heat transfer analysis mainly studies convective, conductive, and radiative heat transfer (such as heat sinks and electronic device cooling), including steady-state and transient thermal analysis. Transient thermal analysis calculates the changes in temperature field distribution over time (such as circuit board thermal management).
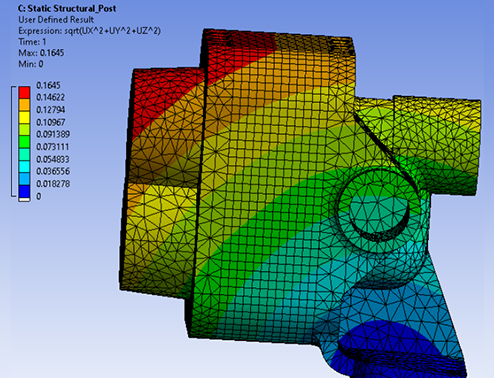
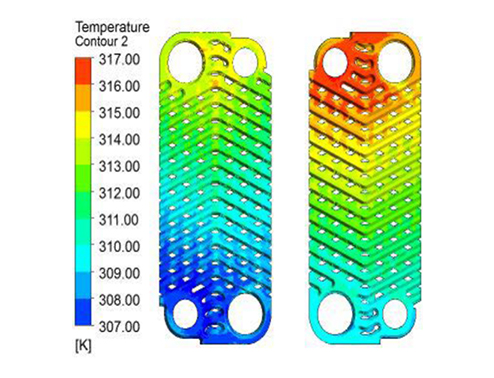
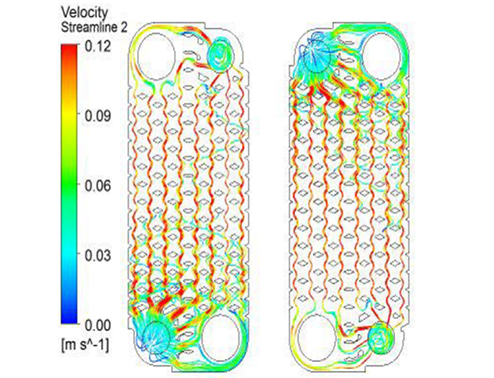
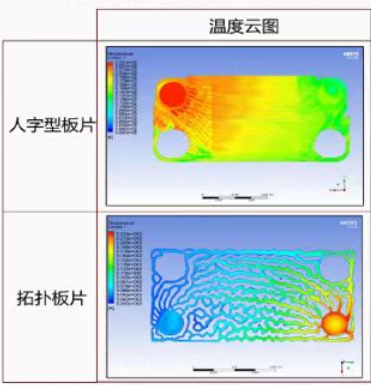
In addition, thermal solid coupling analysis can be conducted to analyze the structural stress and deformation caused by temperature changes (such as thermal expansion of high-temperature furnaces). The left figure shows the temperature field distribution cloud map of the fluid heat conduction analysis of the radiator plate. Using topological plates can greatly improve the heat dissipation effect and temperature distribution
Uniformity.
Heat exchanger design
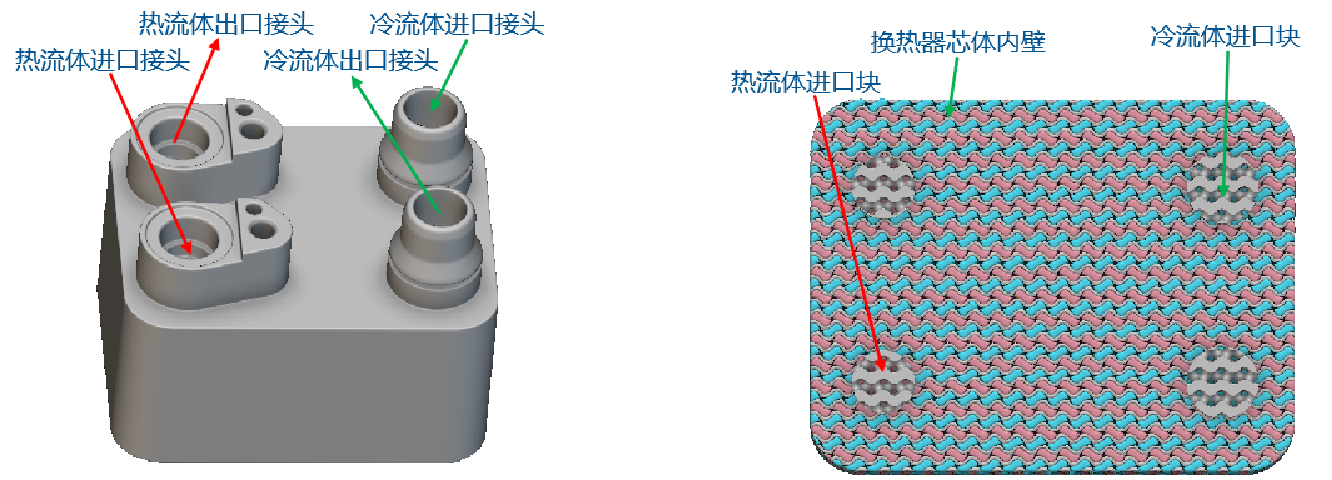
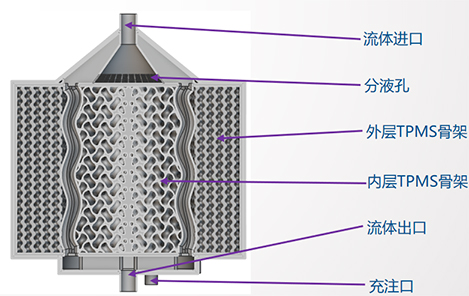
The process of verifying the design of traditional heat exchangers is quite lengthy, and there are limitations in the structural design and manufacturing process of components, which can only develop regular heat exchange structures; Traditional heat exchangers cannot meet the high requirements and performance of heat exchange in fields such as aerospace, automotive and marine, electronic devices, etc. Additive manufacturing technology has matured from the aerospace field and expanded to industries such as biomedicine and automobiles, providing feasibility for the manufacturing of complex lattice structures and biomimetic structures. This enables the application of three period minimal surface structures, biomimetic structures, lattice structures, etc. in new heat exchangers. Jiangsu Yangwang is committed to providing integrated solutions for the design, simulation, and manufacturing of high-performance heat exchangers based on additive manufacturing
Heat exchanger design
Phase change energy storage technology utilizes phase change materials to absorb or release a large amount of latent heat during the phase change process to achieve energy storage and release. Traditional phase change energy storage devices typically use simple packaging structures, such as encapsulating phase change materials in metal containers. This structure has the following issues:
Low thermal conductivity, short cycle life, and single structure. In response to the problems in the field of phase change energy storage, Jiangsu Yangwang provides the design and manufacturing of energy storage devices based on additive manufacturing integrated molding, which can be based on TPMS structure, porous structure, lattice structure, etc.
Test and verify capability
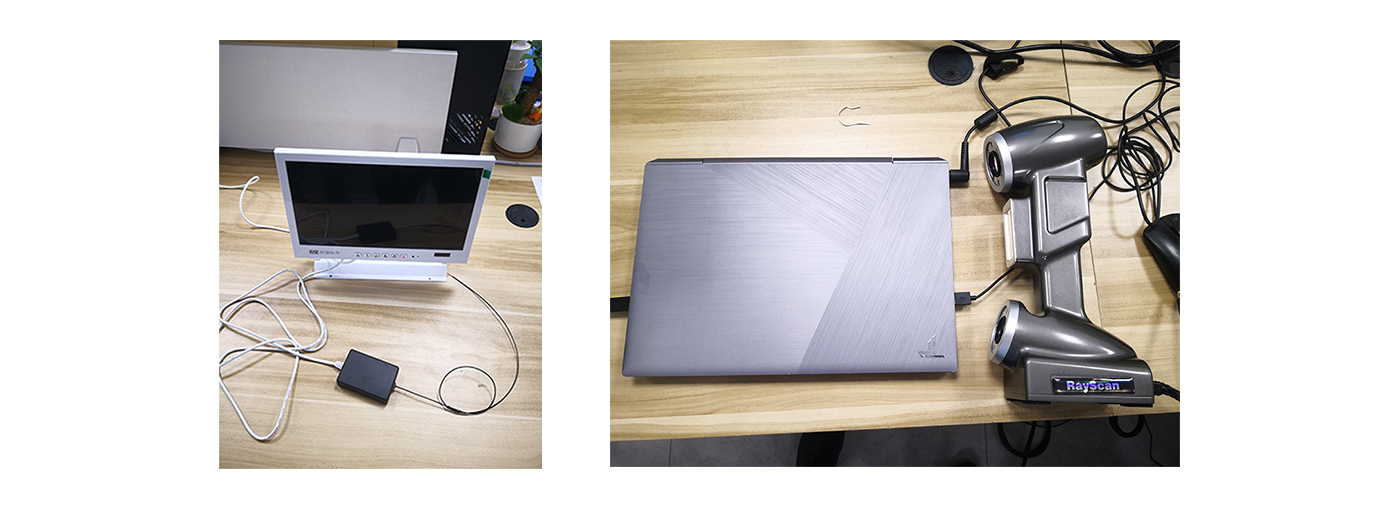
Internal channel polishing technology, abrasive flow+1.2mm flexible endoscope+roughness meter. The RayScan551 handheld 3D scanner can achieve reverse modeling.
Reverse flow test bench, airtight and hydraulic test bench, liquid flow test bench.




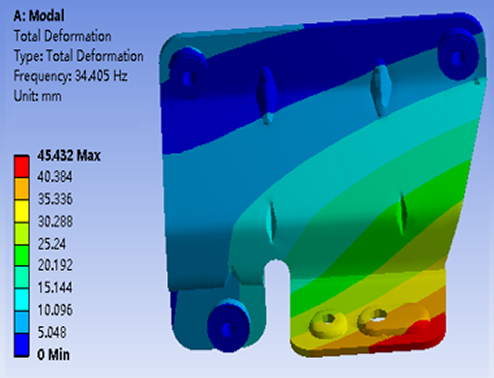
 Stiffness-to-Weight
ratio
Stiffness-to-Weight
ratio